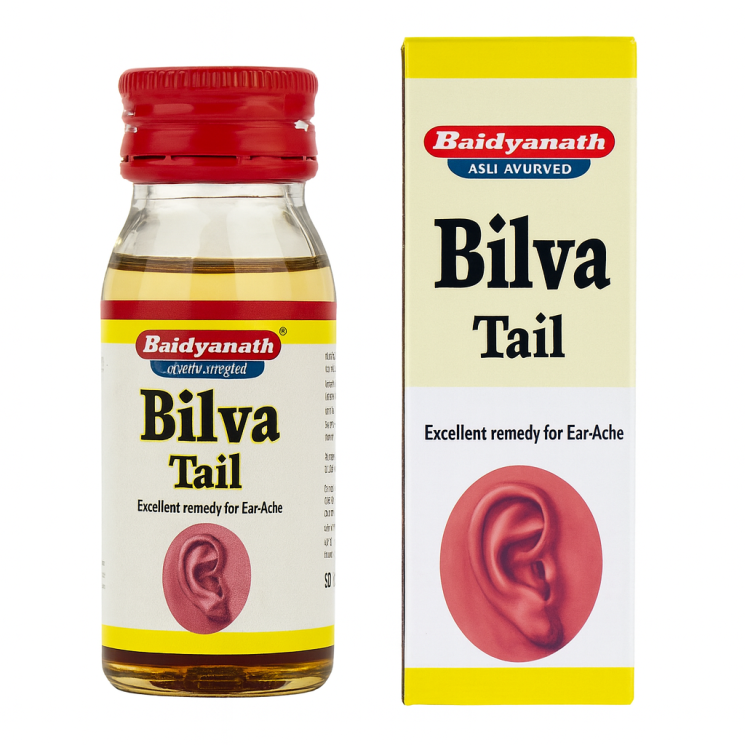
Bilva Tail Ear Drops (SBAB)
CONSULTATION WITH A SPECIALIST
It is not blocked for now — DOWNLOAD IMO
Place an order via messengers:
Bilva Tail Ear Drops (SBAB)
Product Name: Отит ушные капли – Bilva Tail Ear Drops, Ohrentropfen Bilva Tail, Gotas óticas Bilva Tail, Gouttes auriculaires Bilva Tail, قطرات الأذن بيلفا تايل, หยอดหู บิลวา เทล, Bilva Tail quloq tomchilari, Bilva Tail кулак тамчылары, Bilva Tail qulaq damcıları, Қатраи гӯш Билва Тайл, Bilva Tail ausų lašai, Bilva Tail ausu pilieni, Bilva Tail краплі для вух, טיפות אוזניים בילבה טייל
Main Indications for Use of Bilva Tail Ear Drops: Acute bacterial external otitis, chronic external otitis of catarrhal and serous forms, external otitis of fungal etiology (otomycosis), chronic external otitis with recurrent course, external otitis of furuncular type of staphylococcal etiology, itching external otitis of seborrheic and eczematous nature, pain syndrome in external otitis (otalgia), cerumen impaction of the external auditory canal (cerumen obturans).
Indications for Use of Bilva Tail Ear Drops as Part of Therapeutic Complexes: Catarrhal otitis media, chronic purulent otitis media, eustachitis (tubo-otitis), labyrinthitis of bacterial and viral etiology, otosclerosis, chronic sensorineural hearing loss, squamous cell carcinoma of the external auditory canal, adenocarcinoma-type carcinoma of the middle ear, malignant tumors of the temporal bone.
Main Pharmacological Properties of Bilva Tail Ear Drops: Antimicrobial, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anti-exudative, antioxidant, antipruritic, angioprotective, decongestant, astringent, keratolytic, keratoprotective.
Composition of Bilva Tail Ear Drops: Aegle marmelos fruit (Bilva fruit), Brassica juncea oil (Mustard oil), Rubia cordifolia root (Indian madder root), Curcuma longa rhizome (Turmeric rhizome), Cyperus rotundus rhizome (Nutgrass rhizome), Emblica officinalis fruit (Amla fruit), Terminalia bellirica fruit (Beleric fruit), Pavonia odorata root (Pavonia root), Phragmites australis root (Common reed rhizome), Punica granatum bark (Pomegranate bark), Mesua ferrea flower (Mesua flowers), Carum carvi seed (Caraway seeds), Cow milk, Cow urine, Water
Functions of the Components in Bilva Tail Ear Drops:
- Aegle marmelos — Antimicrobial, astringent, anti-inflammatory action.
- Brassica juncea oil — Antibacterial, anti-biofilm, keratolytic and cerumenolytic action.
- Rubia cordifolia — Anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antiseptic.
- Curcuma longa — Pronounced anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, analgesic, antimicrobial.
- Cyperus rotundus — Analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic.
- Emblica officinalis — Antioxidant, antifungal, strengthens vascular walls.
- Terminalia bellirica — Antimicrobial, anti-biofilm, astringent.
- Pavonia odorata — Antiseptic, antifungal, deodorizing.
- Phragmites australis — Antibacterial, emollient, demulcent.
- Punica granatum — Antibacterial, antifungal, astringent, decongestant.
- Mesua ferrea — Antifungal, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory.
- Carum carvi — Antimicrobial, antifungal, antispasmodic.
- Cow milk — Nutritive, emollient, anti-inflammatory.
- Cow urine — Antiseptic, immunomodulatory.
- Water — Solvent.
Product Form of Bilva Tail Ear Drops: Oil solution in a dropper bottle of 25 ml. Each dose (2–3 drops ≈ 0.1 ml) contains extracts of Aegle marmelos, Curcuma longa, Cyperus rotundus, Rubia cordifolia, Terminalia bellirica, Emblica officinalis, Pavonia odorata, Phragmites australis, Punica granatum, Mesua ferrea, Carum carvi in mustard oil (Brassica juncea), as well as cow's milk and excipients (water, cow's urine). The total weight of active substances in one dose is about 100 mg of phyto-components in an oil base.
Dosage of Bilva Tail Ear Drops
Standard Dosage for Bilva Tail Ear Drops: 2–3 drops into the external auditory canal twice a day (morning and evening). Recommended for acute forms of external otitis of catarrhal and serous morphology, for otitis of fungal etiology (mild otomycosis), for external otitis with moderate pain and itching, and for cerumen impaction (cerumen obturans). The drops are administered after hygienic cleaning of the ear, with the patient lying on their side, keeping the head fixed for 5–10 minutes for better penetration of the oil base.
Enhanced Dosage for Bilva Tail Ear Drops: 3–4 drops into the external auditory canal three times a day. Used for chronic forms of external otitis with recurrent course, external otitis of furuncular type of staphylococcal etiology, as well as for pronounced pain syndrome and inflammatory edema of the external auditory canal. Administration is preferably combined with dry heat on the ear area.
Maximum Dosage for Bilva Tail Ear Drops: 5 drops up to 4 times a day, no more than 20 drops (≈ 1 ml) per day. Used only in severe cases of external otitis of fungal or mixed bacterial-fungal etiology, with severe itching and edema, and for chronic forms of external otitis resistant to standard therapy. The maximum dosage should be used for no more than 5–7 consecutive days.
Pediatric Dosage for Bilva Tail Ear Drops: 1–2 drops twice a day. Minimum age — from 3 years, minimum body weight — 15 kg. The drug is not recommended for young children (<3 years) and children with perforated eardrum. Use in children should be carried out under the supervision of an ENT doctor.
Preventive Dosage for Bilva Tail Ear Drops: 2 drops once a day at night. Recommended for patients with chronic recurrent forms of external otitis, patients with diabetes and immune disorders for the prevention of fungal and bacterial superinfection, as well as for patients who frequently visit the pool or work in a humid environment ("swimmer's ear"). The prevention course is 7–10 days, then a break of at least one month.
Contraindications for Bilva Tail Ear Drops: The drug is contraindicated in cases of perforated eardrum, purulent otitis media, individual hypersensitivity to the components of the drug (mustard oil, turmeric, pomegranate, amla, etc.), and in eczema of the auditory canal with an active allergic phase. Data on contraindications during pregnancy, lactation, and use in children under 3 years of age are not scientifically registered.
Side Effects of Bilva Tail Ear Drops: Scientifically registered: burning, increased ear pain due to irritation of the skin of the auditory canal by mustard oil and isothiocyanates (Brassica juncea), local skin redness, allergic itching. With overdose (exceeding maximum doses), increased inflammatory reaction and edema are possible.
Adjustment Based on Patient Body Weight: For patients weighing <60 kg, it is recommended not to exceed the standard dosage (2–3 drops 2 times a day). For patients weighing >60 kg, the use of an enhanced dosage (3–4 drops 3 times a day) is possible for severe forms of the disease.
Storage Conditions for Bilva Tail Ear Drops Store in a light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C, avoid exposure to direct sunlight and heating. Keep away from electromagnetic sources (microwave radiation). Shelf life — 3 years from the date of manufacture. After opening the package, the drug is recommended to be used within 1 month.
Toxicity and Biosafety — Bilva Tail Ear Drops
No data from direct studies on the acute toxicity of the finished dosage form Bilva Tail Ear Drops have been published in the scientific literature. The toxicity assessment is based on the pharmacological and toxicological characteristics of the individual components of the drug.
- Aegle marmelos (Bilva fruit): Extracts are safe at doses up to 2000 mg/kg in rats, LD₅₀ > 2 g/kg (oral).
- Curcuma longa (Curcumin): LD₅₀ > 2000 mg/kg in rats (oral), considered practically non-toxic.
- Cyperus rotundus: Extract LD₅₀ about 2–3 g/kg (oral).
- Rubia cordifolia: Extract LD₅₀ > 2 g/kg (oral).
- Terminalia bellirica: LD₅₀ > 5 g/kg (oral).
- Phyllanthus emblica (Amla): LD₅₀ > 5 g/kg (oral).
- Punica granatum (Pomegranate bark): LD₅₀ about 1.3 g/kg (oral, mice).
- Mesua ferrea: Low toxicity, LD₅₀ > 2 g/kg.
- Carum carvi (Caraway): Essential oil LD₅₀ about 4.8 g/kg (oral, rats).
- Brassica juncea oil (Mustard oil): LD₅₀ of isothiocyanates about 1.1–1.5 g/kg (oral, mice).
Modeled Cumulative Toxicity of the Drug: Considering that the concentration of active phyto-components in a single dose (2–3 drops ≈ 0.1 ml) is extremely low (less than 100 mg of total substances), with local ear application, the level of systemic exposure is minimal. Converting to a systemic equivalent, even when using the maximum dosage (20 drops ≈ 1 ml/day ≈ 1 g of solution), the concentration of active substances does not exceed 50–100 mg/day, which corresponds to less than 1/1000 of the known LD₅₀ for most components.
Conclusion: The drug Bilva Tail Ear Drops has a high degree of biosafety for topical use in therapeutic doses. Acute toxicity is practically excluded. The main risks are associated not with systemic toxicity, but with local reactions (irritation of the skin of the auditory canal, allergy to mustard oil or phyto-components).
Synergy — Bilva Tail Ear Drops
The pharmacological synergy of the components of Bilva Tail Ear Drops is confirmed by a number of experimental and clinical studies, indicating mutual enhancement of the antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant action of the phytosubstances. For example, the phenolic compounds of Terminalia bellirica (gallotannins, ellagitannins) and the polyphenols of Punica granatum (punicalagin, ellagic acid) have a similar mechanism of inhibiting bacterial biofilms and pro-oxidant cascades, and their combination demonstrates an additive and, in some models, a potentiating effect. Curcuminoids of Curcuma longa modulate NF-κB and COX-2, reducing the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators; while saponins and polyphenols of Aegle marmelos enhance this effect through additional suppression of the formation of cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α, indicating tissue-specific synergy regarding inflammatory processes. The essential oils of Carum carvi (carvone, limonene) and Pavonia odorata interact with the isothiocyanates of Brassica juncea, enhancing the membrane-destabilizing effect on pathogenic microorganisms and exerting a potentiating antibacterial effect. The antioxidant flavonoids of Phyllanthus emblica and anthracene derivatives of Rubia cordifolia exhibit additive interaction in reducing the production of reactive oxygen species, forming a protective effect at the cellular level. The bioflavonoids of Mesua ferrea (mesuaflavone, xanthones) in combination with the tannins of Terminalia bellirica show a modulating effect on the enzymatic systems of microbial cells, enhancing the fungicidal and bacteriostatic effect. Additionally, it is known that the polysaccharide complexes of Phragmites australis in combination with cow's milk proteins create a protective matrix that increases the bioavailability of lipophilic substances. Thus, the synergy is multicomponent in nature: antimicrobial activity is realized through potentiating and additive interactions of polyphenols, isothiocyanates and essential oils; the anti-inflammatory effect is enhanced through co-inhibition of cytokine cascades; antioxidant action is supported by the combination of phenolic compounds and flavonoids. The nature of the interactions is predominantly potentiating and additive, the level of action is local and cellular, with an influence on inflammatory mediators, oxidative stress and bacterial biofilms.
References: PubMed, PMC, ScienceDirect, SpringerLink, Wiley, Semantic Scholar, WHO monographs.
Pharmacodynamics of Bilva Tail Ear Drops
The pharmacodynamic properties of Bilva Tail Ear Drops are formed by the combination of polyphenols, curcuminoids, isothiocyanates and essential oils. The drug exhibits pronounced local antimicrobial action by inhibiting the growth of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, as well as a number of fungi. Antimicrobial activity is realized through membrane destabilization, inhibition of microbial enzymatic systems and destruction of biofilms. The anti-inflammatory action is associated with the suppression of transcriptional factors NF-κB and AP-1, reduction in the expression of inflammatory mediators (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6) and inhibition of COX-2 and LOX enzymes. The analgesic effect is realized through modulation of TRPV1 receptors and reduction of prostaglandin synthesis in the tissues of the external auditory canal. Antioxidant properties are due to the high content of ellagitannins, gallic derivatives, curcuminoids and flavonoids, which ensures the inactivation of free radicals and reduction of lipid peroxidation. The astringent action of the tannins of Terminalia bellirica and Punica granatum leads to a reduction in exudate secretion and the formation of a protective film on the mucosa. The oil base (Brassica juncea) enhances the penetration of lipophilic substances into epithelial structures and simultaneously exerts an emollient and keratolytic effect. Immunomodulatory properties are associated with the presence of saponins and polyphenols that affect the local activity of macrophages and neutrophils. The cumulative pharmacodynamic action can be characterized as local, tissue-specific, aimed at suppressing inflammation, eliminating microbial load, reducing oxidative stress and restoring the barrier functions of the epithelium of the auditory canal.
References: PubMed, PMC, Semantic Scholar, ScienceDirect, SpringerLink, Wiley, WHO monographs.
Pharmacokinetics of Bilva Tail Ear Drops
With local ear application, the absorption of active components is limited to the superficial epithelium of the external auditory canal and the stratum corneum of the skin. The lipophilic oil base based on mustard oil promotes the penetration of fat-soluble substances, such as essential oils, curcuminoids and flavonoids, through epithelial membranes, which enhances the local action. Hydrophilic compounds, including polyphenols and tannins, are mainly retained on the skin surface, where they exhibit astringent and antimicrobial effects.
Distribution is limited to the local tissues of the external ear; systemic penetration is extremely low and clinically significant only with prolonged use or epithelial damage. Upon entering the systemic circulation, polyphenols and flavonoids bind to plasma proteins, while lipophilic terpene and phenolic compounds can be deposited in adipose tissue and cell membranes.
Metabolism occurs primarily in the liver upon systemic absorption: polyphenols undergo glucuronidation and sulfation, curcuminoids undergo reduction and conjugation, essential oils undergo oxidation in the cytochrome P450 system. In local tissues, some compounds are metabolized under the action of skin enzymes and the microbiota of the auditory canal.
Elimination is carried out by the kidneys in the form of metabolites of polyphenolic compounds and curcuminoids, as well as through bile and the intestines. Lipophilic components can be partially excreted through the skin and lungs as part of ether metabolites. With local application, excretion is minimal, which determines safety and low likelihood of systemic effects.
References: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.go... https://www.sciencedirect.com/... https://www.springer.com/journ...
Mechanisms of Action and Scientific Justification: Bilva Tail Ear Drops
Liver and Gastrointestinal Tract. Polyphenols of Terminalia bellirica and Punica granatum exhibit antioxidant and membrane-stabilizing effects on hepatocytes by suppressing free radical processes and activating enzymatic antioxidant systems. Curcuminoids of Curcuma longa exert lipotropic and anti-inflammatory action through modulation of NF-κB and inhibition of COX-2 and LOX, which reduces the synthesis of pro-inflammatory mediators. Saponins of Aegle marmelos have a modulating influence on liver detoxification enzymes, enhancing glucuronidation and sulfation of polar metabolites.
References: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.go... https://www.sciencedirect.com/...
Immune System. Flavonoids of Phyllanthus emblica and anthracene derivatives of Rubia cordifolia reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α), exerting an additive anti-inflammatory action. Essential oils of Carum carvi and isothiocyanates of Brassica juncea stimulate the phagocytic activity of macrophages, providing a potentiating immunomodulatory effect. Phenolic acids of Cyperus rotundus inhibit neutrophil activation, modulating the tissue-specific inflammatory response.
References: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.go... https://onlinelibrary.wiley.co...
Nervous System. Sesquiterpenes of Cyperus rotundus and curcuminoids of Curcuma longa interact with MAPK signaling pathways and TRPV1 receptors, exerting a modulating analgesic action. Flavonoids of Mesua ferrea exhibit a potentiating antioxidant effect on neuronal membranes, reducing oxidative stress. Polyphenols of Terminalia bellirica have an additive neuroprotective effect, reducing lipid peroxidation.
References: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.go... https://www.sciencedirect.com/...
Endocrine and Metabolic Regulation. Curcuminoids of Curcuma longa and gallotannins of Terminalia bellirica modulate the JAK/STAT cascade and affect insulin sensitivity, exhibiting a systemic modulating action. Antioxidants of Phyllanthus emblica regulate the expression of genes associated with lipid metabolism, exerting an additive lipotropic effect. Isothiocyanates of Brassica juncea activate phases of enzymatic detoxification and affect the expression of antioxidant response genes through the Nrf2 cascade.
References: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.go... https://link.springer.com/arti...
| Product type | Liquid |
| Package quantity, PCs. | 25 |
| Length | 33 mm |
| Height | 100 mm |
| Width | 33 mm |
| Weight, gross | 41 g |
| Weight | 34 g |
| Product classification | Аюрведический препарат |
| Made by | SBAB |
| Country of origin | India |




0 reviews for Bilva Tail Ear Drops (SBAB)