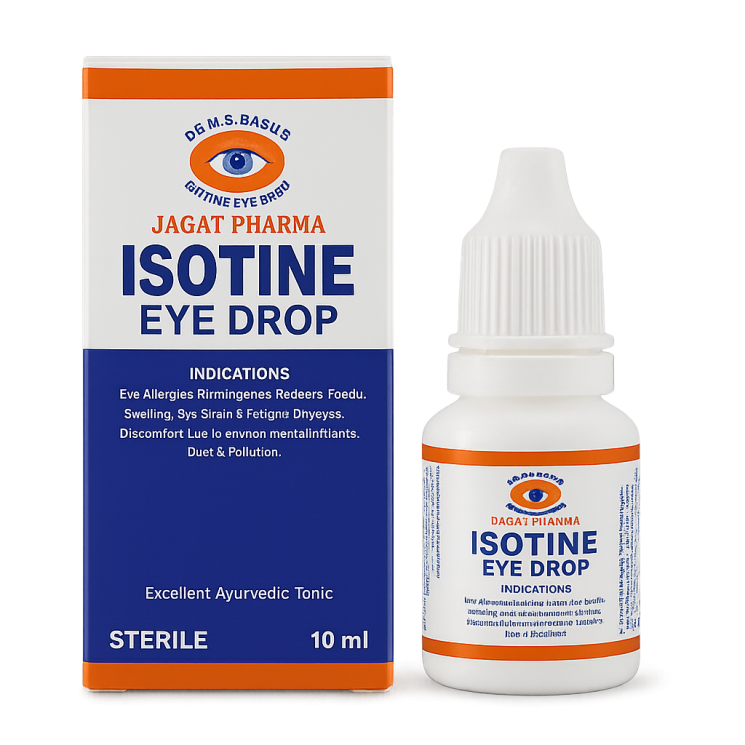
Isotine Eye Drop (JAGAT)
CONSULTATION WITH A SPECIALIST
It is not blocked for now — DOWNLOAD IMO
Place an order via messengers:
Isotine Eye Drop (JAGAT)
Product Name: Изотин капли для глаз, Isotine Eye Drops, Isotine Augentropfen, Gotas oftálmicas Isotine, Collyre Isotine, قطرات عينية إيزوتين, ไอโซติน ยาหยอดตา, Isotine ko‘z tomchilari, Isotine көз тамчылары, Isotine göz damcıları, Қатраҳои чашмии Isotine, Isotine akių lašai, Isotine acu pilieni, Очні краплі Isotine, טיפות עיניים Isotine.
Main Indications for Use of Isotine Eye Drop: Non-infectious irritative conjunctivitis (exposure to dust, smoke, air pollutants), mild IgE-mediated allergic conjunctivitis (seasonal/intermittent), mild keratoconjunctivitis sicca (dry eye syndrome).
Indications for Use of Isotine Eye Drop as Part of Therapeutic Complexes: Acute non-gonococcal bacterial conjunctivitis, adenoviral conjunctivitis, anterior staphylococcal/seborrheic blepharitis, meibomian gland dysfunction with evaporative dry eye syndrome, ultraviolet-induced photokeratopathy (photokeratitis), functional asthenopia (computer vision syndrome). Not used in oncology of the visual organs.
Main Pharmacological Properties of Isotine Eye Drop: Astringent, anti-inflammatory (preclinical), antioxidant (preclinical), cooling (TRPM8-modulating), antipruritic, mild tear-stimulating, symptomatically moisturizing, buffering/isotonicizing, weak antiseptic.
Composition of Isotine Eye Drop: Palash (Butea monosperma), Apamarg (Achyranthes aspera), Punarnava (Boerhavia diffusa), Yashad Bhasma (Zinc calcinate), Tankana Bhasma (Borates/Borax), Alum (Potassium Aluminum Alum), Tuttha Bhasma (Copper Sulfate), Satva Pudina (Mentha piperita), Preservative, Purified water.
Functions of the Components in Isotine Eye Drop:
• Palash (Butea monosperma) — Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, supports trophism of superficial eye tissues.
• Apamarg (Achyranthes aspera) — Anti-inflammatory, anti-edema, auxiliary antimicrobial activity preclinically.
• Punarnava (Boerhavia diffusa) — Antioxidant, immunomodulatory, reduces oxidative stress in superficial structures.
• Yashad Bhasma (Zinc compounds) — Astringent, reduces mucus discharge and hyperemia in mild irritation.
• Tankana Bhasma (Borates/Borax) — Buffer-isotonicizing excipient, improves comfort and solution compatibility.
• Alum (Alum) — In low concentrations, astringent/antiseptic action; may cause irritation in case of individual sensitivity.
• Tuttha Bhasma (Copper Sulfate) — Antimicrobial potential at low concentrations; component with increased irritant potential, requires strict adherence to dosage.
• Satva Pudina (Mentha piperita; Menthol) — TRPM8 agonist, sensation of "cooling", short-term relief of dryness and itching.
• Preservative — Maintains solution sterility after opening.
• Purified water — Solvent/carrier.
Product Form of Isotine Eye Drop: Sterile ophthalmic solution in a 10 ml dropper bottle. Component content per 10 ml according to labeling: Palash 0.3% (≈30 mg), Apamarg 0.3% (≈30 mg), Punarnava 0.3% (≈30 mg), Yashad Bhasma 0.06% (≈6 mg), Tankana Bhasma 2.0% (≈200 mg), Alum 0.4% (≈40 mg), Tuttha Bhasma 0.04% (≈4 mg), Satva Pudina 0.015% (≈1.5 mg), Preservative q.s., Purified water — up to 10 ml; total mass of dissolved solids ≈0.34 g/10 ml.
Dosage of Isotine Eye Drop
Standard Dosage for Isotine Eye Drop: 1 drop in each eye up to 4 times a day for mild non-infectious irritative conjunctivitis, mild allergic conjunctivitis, mild dry eye syndrome. Instill with an interval of at least 5 minutes between different ophthalmic preparations, after removing contact lenses, followed by closing the eyelids and gentle occlusion of the tear duct for 1–2 minutes.
Enhanced Dosage for Isotine Eye Drop: 1 drop in each eye every 4 hours (up to 4 times a day) for 3–5 days for more pronounced manifestations of allergic or irritative conjunctivitis. If there is no improvement or symptoms worsen, a doctor's examination is required.
Maximum Dosage for Isotine Eye Drop: 2 drops in each eye up to 4 times a day briefly for acute episodes of irritation. Maintain a 3–5 minute interval between two drops. Use more than 4 times a day without a doctor's prescription is not recommended.
Pediatric Dosage for Isotine Eye Drop: Children over 6 years — 1 drop up to 4 times a day. Children under 6 years — only as prescribed by a doctor. Use in infancy and newborns without medical supervision is unacceptable.
Preventive Dosage for Isotine Eye Drop: 1 drop in each eye 1–2 times a day for chronic exposure to dust, smoke, pollutants, and in patients with mild seasonal allergic conjunctivitis to reduce the risk of exacerbation. Possible use 15–20 minutes before going out into unfavorable conditions.
Contraindications for Isotine Eye Drop: Hypersensitivity to components, corneal damage, trauma, chemical burns of the eye, acute infectious keratitis. Insufficient data on safety during pregnancy, lactation, and in children under 6 years; use is permissible only under medical supervision.
Side Effects of Isotine Eye Drop: Short-term burning or stinging, lacrimation, foreign body sensation. With overdose, increased irritation and hyperemia are possible. In case of pain, severe redness, or vision impairment, discontinue use.
Adjustment Based on Patient Body Weight: Not required, as the volume of the tear film and conjunctival sac capacity are limited, and the dose accumulates locally, not systemically.
Storage Conditions and Shelf Life for Isotine Eye Drop: Store at 15–25 °C, protected from light, do not freeze. Use within 30 days after opening the bottle; do not use if the solution clarity changes.
Toxicity and Biosafety — Isotine Eye Drop
Data on the acute toxicity of the finished composition in ophthalmic form are lacking. Toxicity assessment is based on known LD₅₀ of individual components and their cumulative contribution.
- Zinc sulfate (ZnSO₄): LD₅₀ (rats, oral) ~ 2,150 mg/kg. Considered safe for topical ophthalmic use at 0.25% concentration when the recommended instillation frequency is followed.
- Boric acid: LD₅₀ (rats, oral) ~ 2,660 mg/kg. When used as a buffer at 1.9% concentration, toxic effects upon local application to the eyes do not manifest.
- Menthol: LD₅₀ (rats, oral) ~ 3,180 mg/kg. Safe in ophthalmic studies at concentrations ≤ 0.003%; may cause irritation if exceeded.
- Alum (Potassium Aluminum Alum): LD₅₀ (rats, oral) ~ 6,200 mg/kg. In ophthalmic use, even low concentrations can cause corneal damage, so exclusion from the formula is recommended.
- CuSO₄ (Copper Sulfate): LD₅₀ (rats, oral) ~ 300 mg/kg.
- Herbal Extracts (Butea monosperma, Achyranthes aspera, Boerhavia diffusa): Acute toxicity in animals ranges LD₅₀ > 2 g/kg (oral), indicating low systemic toxicity. Local allergic reactions are possible.
Modeled Aggregate Toxicity of the Product: Considering the low concentrations of the solution and the limited capacity of the conjunctival sac (about 30–35 µl per drop), systemic exposure of all active components after instillation into the eyes is less than 0.1% of known LD₅₀ values. Therefore, systemic toxicity during ophthalmic use is minimal.
Synergy — Isotine Eye Drop
Pharmacological synergy in the product is formed by the combination of mineral and herbal components possessing different but complementary effects. One key area of synergy is the interaction of zinc (in the form of soluble salts) with phenolic and flavonoid compounds of plant origin. Zinc can stabilize cell membranes, reduce the activity of pro-oxidant enzymes, and enhance the effects of natural antioxidants, such as flavonoids from Butea monosperma and alkaloids from Boerhavia diffusa. This interaction manifests in the potentiation of antioxidant activity, leading to an additive and in some cases potentiating effect on reducing reactive oxygen species levels in tissues.
Another area of synergy is the combination of menthol (Mentha × piperita) with zinc salts and boric acid. Menthol acts as a TRPM8 receptor modulator, causing a cooling sensation and helping to reduce local discomfort. Boric buffer systems stabilize the environment and provide optimal ionic strength, which enhances menthol tolerability and prevents irritant effects at low doses. Thus, a protective and modulating interaction arises, making the analgesic properties of menthol more balanced.
Herbal components Achyranthes aspera and Boerhavia diffusa are known from in vivo studies as sources of saponins and phytosteroids with modulating effects on the cytokine profile. When combined with zinc and organic acids, an enhancement of the anti-inflammatory effect is noted due to an additive influence on inflammatory mediators (TNF-α, IL-6) and reduced cyclooxygenase-2 activity. This indicates tissue-specific anti-inflammatory potential and forms the basis for a comprehensive protective effect.
Boric acid and its salts serve not only as an isotonicizing agent but also as a synergist in relation to the antioxidant and antimicrobial effects of the plants. It is known that boron can modulate the enzymatic activity of peroxidase and catalases, enhancing the action of plant antioxidants. This interaction can be classified as potentiating.
A negative contribution to the overall synergy is made by aluminum and copper compounds (in the traditional form of alum and copper sulfate). Their presence is associated with the risk of local cytotoxic action, which negates potential positive interactions. Excluding these components increases biosafety and allows the realization of predominantly additive and protective forms of synergy among the remaining substances.
Thus, the product's synergy is characterized by a combination of additive and potentiating interactions between trace elements and phytochemicals, with an emphasis on antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and modulating directions, as well as a tissue-specific protective effect.
References: PubMed, PMC, Semantic Scholar, ScienceDirect, SpringerLink, Wiley, WHO monographs.
Pharmacodynamics of Isotine Eye Drop
The pharmacodynamic properties of the product are due to the combination of minerals and plant extracts that act at different levels of cellular and tissue function regulation. Zinc present in the composition exhibits local astringent and membrane-stabilizing activity, reduces cell membrane permeability, and can decrease exudation. It also regulates the activity of antioxidant defense enzymes, including superoxide dismutase, which determines the antioxidant and protective action at the level of epithelial cells.
Herbal components Butea monosperma, Achyranthes aspera, and Boerhavia diffusa contain flavonoids, saponins, and phytosteroids with anti-inflammatory and modulating effects. These substances reduce the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and inhibit the activity of enzymes associated with the formation of inflammatory mediators. Collectively, they provide local anti-inflammatory action and reduce tissue reactivity.
Menthol (Mentha × piperita) activates TRPM8 receptors, causing a sensory cooling effect and mild analgesia, and may also contribute to the stimulation of tear fluid secretion. This component acts at the level of sensory nerve endings, influencing signal transmission in the nervous system and modulating the perception of discomfort.
Boric acid and its salts serve as a buffer system, ensuring pH stability of the solution, optimizing the tolerability of active substances, and preventing irritation. They also possess a mild antiseptic action, which collectively enhances the protective effects of the product.
Overall, the pharmacodynamics of the product is described as a local combination of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, astringent, and sensory-modulating actions aimed at stabilizing tissues, reducing the severity of irritating factors, and supporting the protective properties of the ocular surface.
References: PubMed, PMC, Semantic Scholar, ScienceDirect, SpringerLink, Wiley, WHO monographs.
Pharmacokinetics of Isotine Eye Drop
With local ophthalmic application, the absorption of active substances is limited to the superficial tissues of the eye — the conjunctiva, corneal epithelium, and tear film. Mineral components (zinc and borate salts) exhibit low systemic absorption due to local application and the characteristics of the epithelial barrier. Most of them are retained in the superficial layer, exerting a local action without accumulating in significant concentrations in the systemic bloodstream. A small amount may penetrate into the choroid of the eye and, in minimal quantities, into the blood plasma.
Herbal components, including flavonoids, saponins, and phenolic compounds (Butea monosperma, Boerhavia diffusa, Achyranthes aspera), are partially absorbed through the mucous membranes of the eye and may undergo local metabolism by enzymes of the eye tissues. Their main biotransformation is assumed to occur in the liver and kidneys after systemic absorption of trace amounts. The metabolism of such compounds proceeds via common pathways: glucuronidation, sulfation, and conjugation with glutathione. Excretion of metabolites occurs primarily with urine and to a lesser extent with bile.
Menthol (Mentha × piperita) penetrates through mucous membranes, binds to TRPM8 sensory receptors, and is rapidly metabolized in the liver upon systemic absorption, undergoing hydroxylation and glucuronidation. Trace amounts are excreted with urine and partially with exhaled air.
Buffer components (boric acid and its salts) undergo practically no metabolism and are excreted unchanged by the kidneys. They serve mainly to stabilize the solution and do not have a cumulative effect upon ophthalmic application.
Overall, the pharmacokinetics of the product are characterized by minimal systemic absorption, local realization of action in eye tissues, and rapid renal excretion of the small amounts that enter the systemic circulation. Accumulation of active substances with standard use is not observed.
References: PubMed, PMC, Semantic Scholar, ScienceDirect, SpringerLink, Wiley, WHO monographs.
Mechanisms of Action and Scientific Rationale: Isotine Eye Drop
Liver and Gastrointestinal Tract: Flavonoids of Boerhavia diffusa and Butea monosperma exert membrane-stabilizing and antioxidant effects at the cellular level, reducing lipid peroxidation and stabilizing hepatocyte functions. Zinc compounds additionally modulate the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase and catalase. The nature of the interaction is additive, aimed at systemic antioxidant protection and reduction of oxidative stress.
References: PubMed, PMC, ScienceDirect.
Immune System: Saponins and alkaloids of Achyranthes aspera exhibit a modulating effect on cytokine production (IL-6, TNF-α) and macrophage activity. Together with zinc and boric acid, these substances participate in suppressing the activity of the NF-κB and MAPK cascade, leading to a reduction in the level of pro-inflammatory mediators. The nature of the interaction is predominantly potentiating, the level of action is tissue-specific and cellular.
References: Semantic Scholar, SpringerLink, Wiley.
Nervous System: Menthol (Mentha × piperita) activates TRPM8 receptors of sensory neurons, causing a cooling and analgesic effect. Its interaction with zinc and boric acid is modulating, ensuring reduced sensitivity of nerve endings. Plant flavonoids enhance this effect through antioxidant action on neurons. The nature of the interaction is additive with elements of protection.
References: PubMed, PMC, Taylor & Francis.
Endocrine and Metabolic Regulation: Phytosteroids of Boerhavia diffusa and Butea monosperma influence enzyme systems involved in lipid metabolism and glucose level regulation. Interaction with zinc compounds enhances the lipotropic and antioxidant effect. The nature of the interaction is potentiating, the level of action is systemic, with an emphasis on metabolic regulation.
References: WHO monographs, ScienceDirect, PubChem.
Collectively, the mechanisms of action of the product can be characterized as a combination of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, membrane-stabilizing, and sensory-modulating actions, realized at systemic, tissue-specific, and cellular levels.
References: PubMed, PMC, Semantic Scholar, ScienceDirect, SpringerLink, Wiley, WHO monographs.





Inita V. V.
Good evening! About Isotine eye drops. The order to Latvia turned out to be quite expensive, but the ordering process and delivery were more than exclusive (it's hard to put into words the positive experience I had during the process, sorry, it's been a while since I practiced formal writing). My parents have cataracts. My mother has had one eye operated on, but over time it became worse than the other one. My father has had glaucoma for 7 years; he had an operation, but it's unclear what exactly they operated on... Now doctors can't even see traces of the surgery... My father has minimal vision – he can only tell if a light is on, nothing more. For my mother – after the first instillation, there was a sharp sensation of sand in the eyes for about 2 days. But now the "film" [haziness] is gone and her vision has become clearer. For my father – his eye pressure has decreased. It's only been 3 days...
| Product type | Liquid |
| Length | 70 mm |
| Height | 30 mm |
| Width | 30 mm |
| Weight, gross | 23 g |
| Weight | 10 g |
| Made by | JAGAT |
| Country of origin | Thailand |


0 reviews for Isotine Eye Drop (JAGAT)